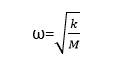PHONONS
Phonon is a quantum of lattice vibrational mechanical
energy. They are basically the ground and excited
states of quantised lattice vibrations of interacting particles.
The
name phonon comes from the Greek word phonē which means voice or sound, as long wave length phonons give rise to
sound.
Atoms
in a crystal lattice can be considered to behave as if they are connected by
tiny springs which makes mechanical waves that carry heat and sound as a result
of executing Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) by their own thermal vibrations and
external forces. A packet of this wave can travel through the crystal with a
definite energy and momentum, which in quantum mechanical terms can be
considered as a particle (phonon).
So, we
can imagine atoms vibrating in SHM as a lattice wave.
Its equation can be
written as,
Where:
k= Restoring force, M= Mass of atom
By Schrödinger’s equation,
On solving, we get the energy Eigen values as,
The energy difference
between two allowed states is  . So we define the basic packets of energy
. So we define the basic packets of energy and momentum
and momentum and these fundamental packets of energy exchanged are called phonons.
and these fundamental packets of energy exchanged are called phonons.
 . So we define the basic packets of energy
. So we define the basic packets of energy and momentum
and momentum and these fundamental packets of energy exchanged are called phonons.
and these fundamental packets of energy exchanged are called phonons.
Phonon
is a quasi- particle, that is something that is not a real particle but can
behave and be considered as one. They are responsible for acoustic properties,
thermal conductivity and heat capacity of solids. Besides, phonons are bosons,
that is they follow Bose-Einstein statistics (Indistinguishable, but not
obeying Pauli’s exclusion principle), which take the crucial role in the super
conducting phenomena (low temperature) as an intermediate particle which makes
electrons slightly attract each other whereas they would have normally repelled.